---
title: Machine states and lifecycle
layout: docs
nav: machines
toc: true
---
Fly Machines go through a series of lifecycle states during creation, updates, shutdown, and deletion. If you're automating deployments, coordinating Machine pools, or writing tools against the Machines API, understanding these states can help you make better decisions.
## Machine state vs. machine version state
Each Machine has a single Machine ID, but every change (like updating the image or resources) creates a new Machine version. It's important to distinguish between:
- Overall Machine state – represents the active version of the Machine.
- Machine version state – represents the state of a specific version of a Machine.
If you query a Machine without specifying a version, the API returns the current active version's state. If you query an older version, the API may return a terminal state like `replaced`.
## Machine state types
### Persistent states
These states remain until you take action (or something fails).
| State | Description |
|-------|-------------|
| `created` | Initial status. Machine has been created but not yet started |
| `started` | Running and network-accessible |
| `stopped` | Exited, either on its own or explicitly stopped |
| `suspended` | Suspended to disk; will attempt to resume on next start |
| `failed` | Machine encountered an error and could not start successfully |
### Transient states
These are short-lived. The Machine will move to a new state automatically.
| State | Description |
|-------|-------------|
| `creating` | Machine is being initialized |
| `starting` | Transitioning from stopped or suspended to started |
| `stopping` | Transitioning from started to stopped |
| `restarting` | Machine is restarting |
| `suspending` | Transitioning from started to suspended |
| `destroying` | User asked for the Machine to be completely removed |
| `launch_failed` | Machine failed to launch; will transition to destroyed |
| `updating` | Machine is being updated to a new version |
| `replacing` | User-initiated configuration change (image, VM size, etc.) in progress |
### Terminal states
These are final states that a Machine or its version won't exit from.
| State | Description |
|-------|-------------|
| `destroyed` | No longer exists |
| `replaced` | Machine version was replaced by a newer one (applies to version-specific queries only). If you query an older version by ID, the API will always return replaced for that version, even if the Machine is currently running. |
| `migrated` | Machine has been moved to a new host; previous version is no longer active |
## Machine state lifecycle diagrams
### Overall Machine state lifecycle
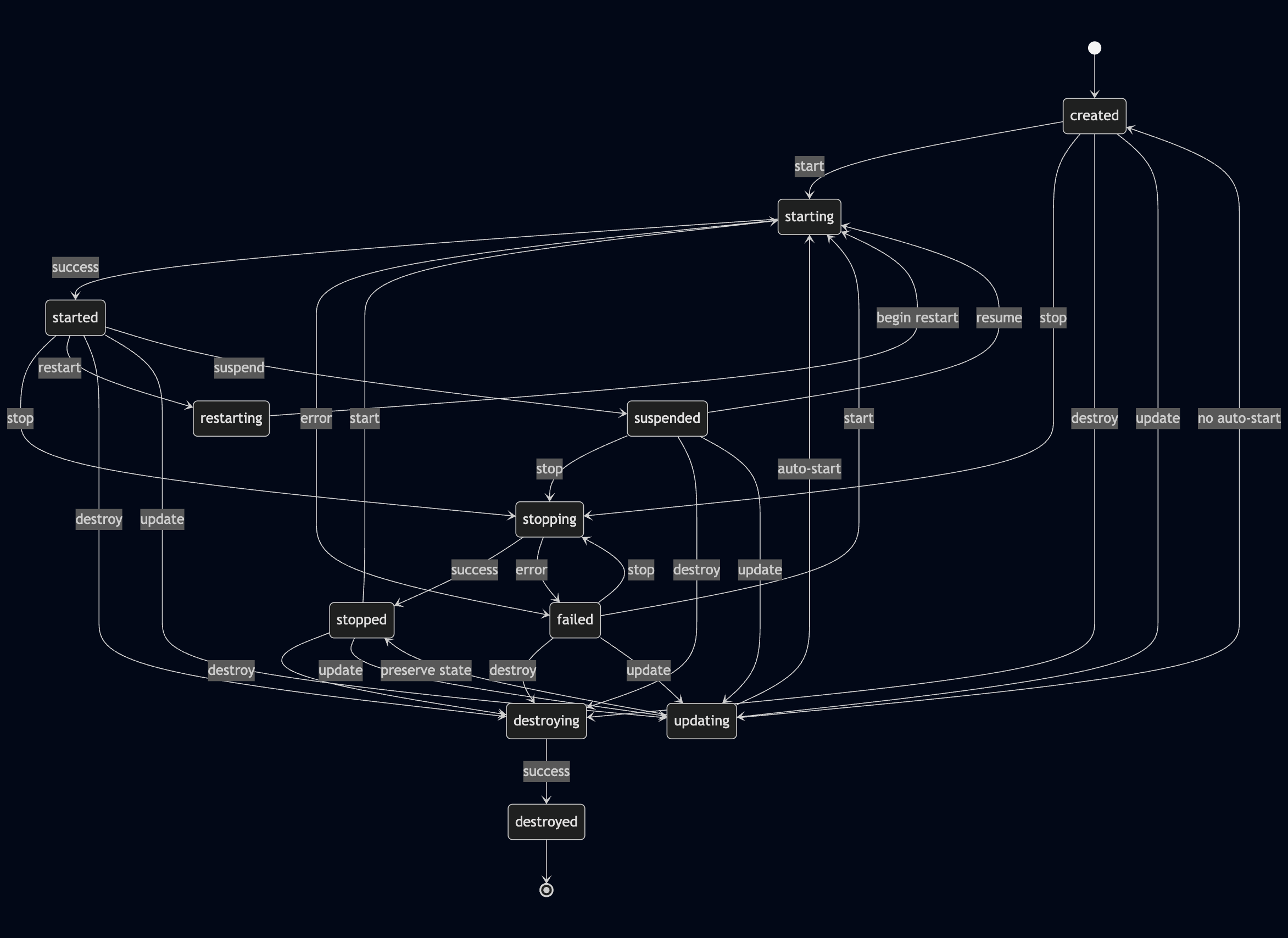
### Machine version state transitions
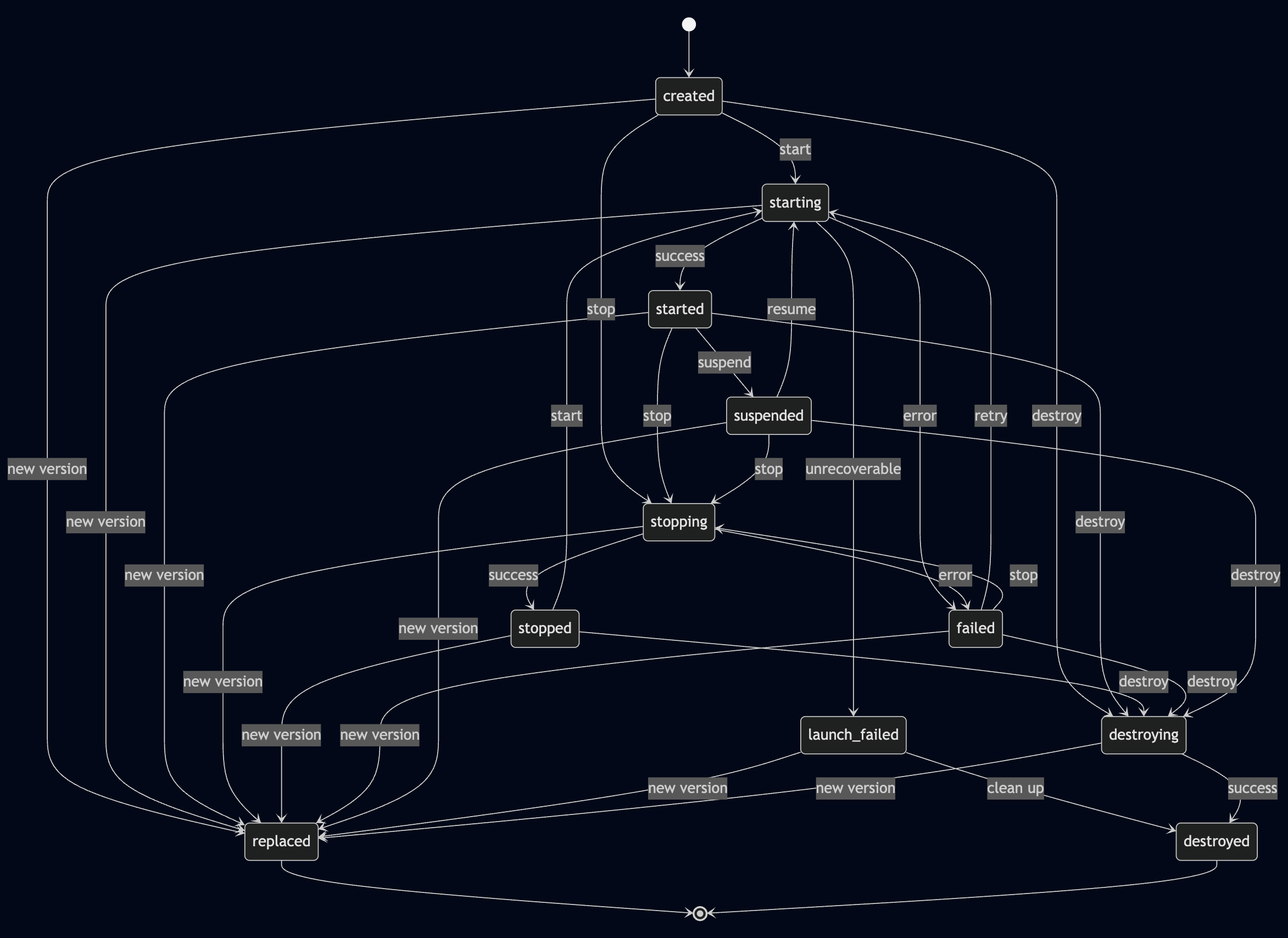
## Update and versioning behavior
When you update a Machine:
1. A new Machine version is created with the updated configuration.
2. The previous version is marked as `replaced`.
3. The new version becomes the active version and:
- May stay in `created` if `skip_launch` is set to true.
- May transition to `started` by default.
- May transition to `stopped`, depending on how the update was triggered and the config used.
Machines are launched automatically upon creation or after an update unless `skip_launch` is explicitly set. This flag allows you to create or update a Machine without starting it immediately.
If you query an old version by version ID, you may see `replaced`. To always get the current state, query the Machine without specifying a version.
## Diagnosing stuck Machines
If a Machine stays in a transient state for an extended time, it might be stuck ("wedged"). The following thresholds can help you decide:
- `starting`, `stopping`, `restarting`, or `destroying` > 5 minutes (this can depend on the configured `kill_timeout`)
- `updating` > 10 minutes
To troubleshoot:
1. Check machine events via the Machines API.
2. Try stopping and starting the Machine.
3. If needed, contact Fly.io support with the Machine ID.
## Important Machine state considerations
- `replaced` applies only to old versions and is terminal for that version. If you query an older version by ID, the API will always return `replaced` for that version, even if the Machine is currently running.
- `migrated` indicates the Machine was moved to a new host and is no longer active.
- Machines in `suspended` preserve memory and disk state, and resume faster than `stopped`.
- The `launch_failed` state is usually unrecoverable and transitions to `destroyed`.
- Machines in `failed` may be recoverable. You can try restarting, stopping, or destroying them.
## Related docs
- [Machines API reference](/docs/machines/api/)
- [Working with Machines](/docs/machines/)
- [Fly machine update command](/docs/machines/flyctl/fly-machine-update/)
Machine states and lifecycle
Fly Machines go through a series of lifecycle states during creation, updates, shutdown, and deletion. If you’re automating deployments, coordinating Machine pools, or writing tools against the Machines API, understanding these states can help you make better decisions.
Machine state vs. machine version state
Each Machine has a single Machine ID, but every change (like updating the image or resources) creates a new Machine version. It’s important to distinguish between:
Overall Machine state – represents the active version of the Machine.
Machine version state – represents the state of a specific version of a Machine.
If you query a Machine without specifying a version, the API returns the current active version’s state. If you query an older version, the API may return a terminal state like replaced.
Machine state types
Persistent states
These states remain until you take action (or something fails).
State
Description
created
Initial status. Machine has been created but not yet started
started
Running and network-accessible
stopped
Exited, either on its own or explicitly stopped
suspended
Suspended to disk; will attempt to resume on next start
failed
Machine encountered an error and could not start successfully
Transient states
These are short-lived. The Machine will move to a new state automatically.
State
Description
creating
Machine is being initialized
starting
Transitioning from stopped or suspended to started
stopping
Transitioning from started to stopped
restarting
Machine is restarting
suspending
Transitioning from started to suspended
destroying
User asked for the Machine to be completely removed
launch_failed
Machine failed to launch; will transition to destroyed
updating
Machine is being updated to a new version
replacing
User-initiated configuration change (image, VM size, etc.) in progress
Terminal states
These are final states that a Machine or its version won’t exit from.
State
Description
destroyed
No longer exists
replaced
Machine version was replaced by a newer one (applies to version-specific queries only). If you query an older version by ID, the API will always return replaced for that version, even if the Machine is currently running.
migrated
Machine has been moved to a new host; previous version is no longer active
Machine state lifecycle diagrams
Overall Machine state lifecycle
Machine version state transitions
Update and versioning behavior
When you update a Machine:
A new Machine version is created with the updated configuration.
The previous version is marked as replaced.
The new version becomes the active version and:
May stay in created if skip_launch is set to true.
May transition to started by default.
May transition to stopped, depending on how the update was triggered and the config used.
Machines are launched automatically upon creation or after an update unless skip_launch is explicitly set. This flag allows you to create or update a Machine without starting it immediately.
If you query an old version by version ID, you may see replaced. To always get the current state, query the Machine without specifying a version.
Diagnosing stuck Machines
If a Machine stays in a transient state for an extended time, it might be stuck (“wedged”). The following thresholds can help you decide:
starting, stopping, restarting, or destroying > 5 minutes (this can depend on the configured kill_timeout)
updating > 10 minutes
To troubleshoot:
Check machine events via the Machines API.
Try stopping and starting the Machine.
If needed, contact Fly.io support with the Machine ID.
Important Machine state considerations
replaced applies only to old versions and is terminal for that version. If you query an older version by ID, the API will always return replaced for that version, even if the Machine is currently running.
migrated indicates the Machine was moved to a new host and is no longer active.
Machines in suspended preserve memory and disk state, and resume faster than stopped.
The launch_failed state is usually unrecoverable and transitions to destroyed.
Machines in failed may be recoverable. You can try restarting, stopping, or destroying them.